When you use repository pattern you want your DB operations to be in Data Layer, but when you create ASP.NET Core site with Individual User Accounts, Visual Studio automatically creates ApplicationDbContext in your presentation layer and binds your presentation layer with your data layer.
Here we will try to decouple user management from presentation layer, and move DB operations (inserting / updating / deleting of users / roles / logins… ) to where they belong, data layer.
Note: I’m using VS 2017 and .NET Core 2.0
Define the solution
Here we are going to setup our solution for repository pattern. This is pretty straightforward
Create new ASP.NET Core project
- File -> New -> Project
- Select ASP.NET Core Web Application
- Set the name of your project, for this post I will use DLAuth
- Choose Web Application (MVC)
- Click on Change Authentication
- Select Individual User Accounts, and Store user accounts in-app
Add Data Layer project
- Right-click on solution name (Solution ‘DLAuth’) and add new project
- Select Class Library (.NET Core)
- For simplicity I will name this project DL
- Create the following folders in DL project: Models, Interfaces, Repositories, Concrete
Add Business Layer
- Right-click on solution name (Solution ‘DLAuth’) and add new project
- Select Class Library (.NET Core)
- For simplicity I will name this project BL
- Create the following folders in BL project: Models, Interfaces, Services, Stores, Mappings
After this steps you should have project structure similar to this
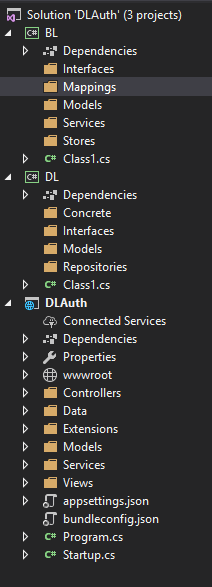
Now we can start implementing the actual logic.
Data Layer - DL Project
We are starting with our data layer implementation
1. Defining Models
Create following models in DL project in Models folder.
User model:
public class User : ClaimsIdentity {
public string Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string NormalizedUserName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string NormalizedEmail { get; set; }
public bool EmailConfirmed { get; set; }
public string PasswordHash { get; set; }
public string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
public bool PhoneNumberConfirmed { get; set; }
public string PhotoUrl { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string ConcurrencyStamp { get; set; }
public string SecurityStamp { get; set; }
public DateTime? RegistrationDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? LastLoginDate { get; set; }
public bool LockoutEnabled { get; set; }
public DateTime? LockoutEndDateTimeUtc { get; set; }
public bool TwoFactorEnabled { get; set; }
public int AccessFailedCount { get; set; }
}
Role model:
public class Role {
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string NormalizedName { get; set; }
public string ConcurrencyStamp { get; set; }
}
UserClaim model:
public class UserClaim {
public string Id { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string ClaimType { get; set; }
public string ClaimValue { get; set; }
}
UserLogin model:
public class UserLogin {
public string LoginProvider { get; set; }
public string ProviderKey { get; set; }
public string UserId { get; set; }
public string ProviderDisplayName { get; set; }
}
2. Defining Repository Interfaces
Now we need to define the interfaces for the repositories that we will be using. Place the following interfaces in DL project in Interfaces folder
IUserRepository: for managing users
public interface IUsersRepository {
Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<User> FindByIdAsync(string userId);
Task<User> FindByNameAsync(string normalizedUserName);
Task<User> FindByEmailAsync(string normalizedEmail);
Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IEnumerable<User>> GetAllUsers();
void Dispose();
}
IRolesRepository: for managing roles
public interface IRolesRepository {
Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<Role> FindByIdAsync(string roleId);
Task<Role> FindByNameAsync(string normalizedRoleName);
Task<IEnumerable<Role>> GetAllRoles();
void Dispose();
}
IUsersRolesRepository: for managing user - role relations
public interface IUsersRolesRepository {
Task AddToRoleAsync(User user, string roleId);
Task RemoveFromRoleAsync(User user, string roleId);
Task<IList<string>> GetRolesAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
void Dispose();
}
IUsersClaimsRepository: managing claims
public interface IUsersClaimsRepository {
Task<IList<Claim>> GetClaimsAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task AddClaimsAsync(User user, IEnumerable<Claim> claims);
Task ReplaceClaimAsync(User user, Claim claim, Claim newClaim);
void Dispose();
}
IUsersLoginsRepository: managing logins
public interface IUsersLoginsRepository {
Task AddLoginAsync(User user, UserLoginInfo login);
Task RemoveLoginAsync(User user, string loginProvider, string providerKey);
Task<IList<UserLoginInfo>> GetLoginsAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<User> FindByLoginAsync(string loginProvider, string providerKey,
CancellationToken cancellationToken);
void Dispose();
}
Let’s define our database connection interface here
IDatabaseConnection: manages DB object
public interface IDatabaseConnectionService : IDisposable {
Task<SqlConnection> CreateConnectionAsync();
SqlConnection CreateConnection();
}
3. Implementing Repositories
Now we need to implement the interfaces we defined previously. Place the following classes in DL project in Repositories folder. For executing SQL queries I’m using Dapper, but you can use whatever suits your needs. Note: to keep this post simple I will post only snippets here and link to the whole implementations on GitHub
UsersRepository (link)
public class UsersRepository : IUsersRepository
{
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
public UsersRepository(IDatabaseConnectionService sqlConnection)
{
_sqlConnection = sqlConnection.CreateConnection();
}
public Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
const string command = "INSERT INTO ...";
var rowsInserted = Task.Run(() => _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new
{
user.Id,
user.FirstName,
user.LastName,
user.UserName,
user.NormalizedUserName,
user.Email,
...
}), cancellationToken).Result;
return Task.FromResult(rowsInserted.Equals(1) ? IdentityResult.Success : IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError
{
Code = string.Empty,
Description = $"The user with email {user.Email} could not be inserted in the dbo.Users table."
}));
}
public Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
const string command = "DELETE " +
"FROM dbo.Users " +
"WHERE Id = @Id;";
....
RolesRepository (link)
public class RolesRepository : IRolesRepository {
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
public RolesRepository(IDatabaseConnectionService sqlConnection) {
_sqlConnection = sqlConnection.CreateConnection();
}
public Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken) {
const string command = "INSERT INTO dbo.Roles " +
"VALUES (@Id, @ConcurrencyStamp, @Name, @NormalizedName);";
var rowsInserted = Task.Run(() => _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new {
role.Id,
role.ConcurrencyStamp,
role.Name,
role.NormalizedName
}), cancellationToken).Result;
return Task.FromResult(rowsInserted.Equals(1) ? IdentityResult.Success : IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError {
Code = string.Empty,
Description = $"The role with ..."
}));
}
public Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken) {
const string command = "UPDATE dbo.Roles ...";
var rowsUpdated = Task.Run(() => _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new {
role.ConcurrencyStamp,
role.Name,
role.NormalizedName,
role.Id
}), cancellationToken).Result;
return Task.FromResult(rowsUpdated.Equals(1) ? IdentityResult.Success : IdentityResult.Failed(new IdentityError {
Code = string.Empty,
Description = $"The role with name {role.Name} could not be updated in the dbo.Roles table."
}));
}
....
UsersRolesRepository (link)
public class UsersRolesRepository : IUsersRolesRepository {
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
public UsersRolesRepository(IDatabaseConnectionService sqlConnection) {
_sqlConnection = sqlConnection.CreateConnection();
}
public Task AddToRoleAsync(User user, string roleId) {
const string command = "INSERT INTO dbo.UsersRoles " +
"VALUES (@UserId, @RoleId);";
return _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new {
UserId = user.Id,
RoleId = roleId
});
}
public Task RemoveFromRoleAsync(User user, string roleId) {
const string command = "DELETE " +
"FROM dbo.UsersRoles " +
"WHERE UserId = @UserId AND RoleId = @RoleId;";
return _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new {
UserId = user.Id,
RoleId = roleId
});
}
....
UsersClaimsRepository (link)
public class UsersClaimsRepository : IUsersClaimsRepository {
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
public UsersClaimsRepository(IDatabaseConnectionService sqlConnection) {
_sqlConnection = sqlConnection.CreateConnection();
}
public Task<IList<Claim>> GetClaimsAsync(User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken) {
const string command = "SELECT * " +
"FROM dbo.UsersClaims " +
"WHERE UserId = @UserId;";
var userClaims = Task.Run(() => _sqlConnection.QueryAsync<UserClaim>(command, new {
UserId = user.Id
}), cancellationToken).Result;
return Task.FromResult<IList<Claim>>(userClaims.Select(e => new Claim(e.ClaimType, e.ClaimValue)).ToList());
}
....
UsersLoginsRepository (link)
public class UsersLoginsRepository : IUsersLoginsRepository {
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
public UsersLoginsRepository(IDatabaseConnectionService sqlConnection) {
_sqlConnection = sqlConnection.CreateConnection();
}
public Task AddLoginAsync(User user, UserLoginInfo login) {
const string command = "INSERT INTO dbo.UsersLogins " +
"VALUES (@LoginProvider, @ProviderKey, @UserId, @ProviderDisplayName);";
return _sqlConnection.ExecuteAsync(command, new {
login.LoginProvider,
login.ProviderKey,
UserId = user.Id,
login.ProviderDisplayName
});
}
....
3. Implementing database connection class
We need to define class for creating DB connections
DatabaseConnectionService
public class DatabaseConnectionService : IDatabaseConnectionService {
private SqlConnection _sqlConnection;
private readonly string _connectionString;
public DatabaseConnectionService(string connectionString) {
_connectionString = connectionString;
}
public async Task<SqlConnection> CreateConnectionAsync() {
_sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(_connectionString);
await _sqlConnection.OpenAsync();
return await Task.FromResult(_sqlConnection);
}
public SqlConnection CreateConnection() {
_sqlConnection = new SqlConnection(_connectionString);
_sqlConnection.Open();
return _sqlConnection;
}
public void Dispose() {
if (_sqlConnection == null) {
return;
}
_sqlConnection.Dispose();
_sqlConnection = null;
}
}
We have succesfully implemented our Data Layer.
Now your data layer should look like this.
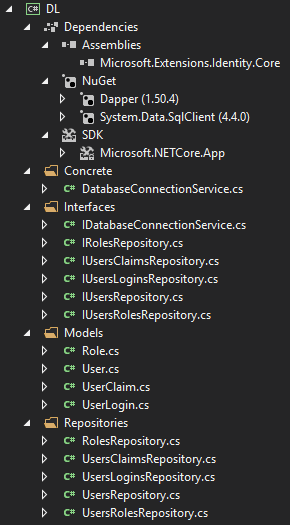
Business Layer - BL Project
Next we need to define our Store’s for managing User’s and Role’s
1. Defining Models
We need User and Role model in BL project in Models folder. Copy them from DL.Models but make sure to change the namespace to BL.Models
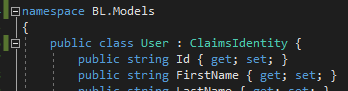
2. Defining Interfaces
In BL for now we only need two interfaces IUserStore and IRoleStore Put them in BL.Interfaces folder.
IUserStore (link)
public interface IUserStore {
IQueryable<BL.Models.User> Users();
Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(BL.Models.User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(BL.Models.User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<BL.Models.User> FindByIdAsync(string userId, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<BL.Models.User> FindByNameAsync(string normalizedUserName, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<string> GetNormalizedUserNameAsync(BL.Models.User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<string> GetUserIdAsync(BL.Models.User user, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
....
IRoleStore (link)
public interface IRoleStore {
IQueryable<BL.Models.Role> Roles();
Task<IdentityResult> CreateAsync(BL.Models.Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> UpdateAsync(BL.Models.Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
Task<IdentityResult> DeleteAsync(BL.Models.Role role, CancellationToken cancellationToken);
....
3. Implementing IUserStore and IRoleStore
In order for our stores to adhere to ASP.NET Identity requirements we also need to implement the following interfaces from Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity
- UserStore: IQueryableUserStore, IUserEmailStore, IUserLoginStore, IUserPasswordStore, IUserPhoneNumberStore, IUserTwoFactorStore, IUserSecurityStampStore, IUserClaimStore, IUserLockoutStore, IUserRoleStore, IUserStore
- RoleStore: IQueryableRoleStore
UserStore (link)
public class UserStore :
IQueryableUserStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserEmailStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserLoginStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserPasswordStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserPhoneNumberStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserTwoFactorStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserSecurityStampStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserClaimStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserLockoutStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserRoleStore<BL.Models.User>,
IUserStore,
IUserStore<BL.Models.User> {
private readonly IUsersRepository _usersRepository;
private readonly IUsersRolesRepository _usersRolesRepository;
private readonly IRolesRepository _rolesRepository;
private readonly IUsersClaimsRepository _usersClaimsRepository;
private readonly IUsersLoginsRepository _usersLoginsRepository;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
public UserStore(IUsersRepository usersRepository,
IUsersRolesRepository usersRolesRepository,
IRolesRepository rolesRepository,
IUsersClaimsRepository usersClaimsRepository,
IUsersLoginsRepository usersLoginsRepository,
IMapper mapper) {
_usersRepository = usersRepository;
_usersRolesRepository = usersRolesRepository;
_rolesRepository = rolesRepository;
_usersClaimsRepository = usersClaimsRepository;
_usersLoginsRepository = usersLoginsRepository;
_mapper = mapper;
}
....
RoleStore (link)
public class RoleStore : IQueryableRoleStore<BL.Models.Role>, IRoleStore {
private readonly IRolesRepository _rolesRepository;
private readonly IMapper _mapper;
public RoleStore(IRolesRepository rolesRepository, IMapper mapper) {
_rolesRepository = rolesRepository;
_mapper = mapper;
}
public IQueryable<BL.Models.Role> Roles => _mapper.Map<IQueryable<BL.Models.Role>>(Task.Run(() => _rolesRepository.GetAllRoles()).Result.AsQueryable());
IQueryable<BL.Models.Role> IRoleStore.Roles() {
return Roles;
}
....
4. Configure AutoMapper
First install AutoMapper from NuGet. Then in Mappings folder create MappingProfile.cs
public class MappingProfile : Profile {
public MappingProfile() {
CreateMap<DL.Models.User, BL.Models.User>().ReverseMap();
CreateMap<DL.Models.Role, BL.Models.Role>().ReverseMap();
CreateMap<Task<DL.Models.Role>, Task<BL.Models.Role>>().ReverseMap();
CreateMap<Task<DL.Models.User>, Task<BL.Models.User>>().ReverseMap();
}
}
Your Business Layer should look like this:
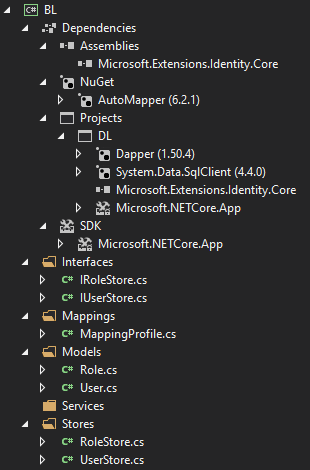
Presentation Layer - DLAuth Project
Now we need to configure our ASP.NET Core site to use our implementation.
1. Delete existing implementation
- Delete Data folder.
- From Models delete ApplicationUser.cs
2. Define Infrastructure
Create Infrastructure folder in your presentation layer (DLAuth Project). And define following classes:
UserManager
public class UserManager : UserManager<BL.Models.User> {
public UserManager(IUserStore<BL.Models.User> store,
IOptions<IdentityOptions> optionsAccessor,
IPasswordHasher<BL.Models.User> passwordHasher,
IEnumerable<IUserValidator<BL.Models.User>> userValidators,
IEnumerable<IPasswordValidator<BL.Models.User>> passwordValidators,
ILookupNormalizer keyNormalizer,
IdentityErrorDescriber errors,
IServiceProvider services,
ILogger<UserManager<BL.Models.User>> logger)
: base(store,
optionsAccessor,
passwordHasher,
userValidators,
passwordValidators,
keyNormalizer,
errors,
services,
logger) {
}
}
RoleManager
public class RoleManager : RoleManager<BL.Models.Role> {
public RoleManager(IRoleStore<BL.Models.Role> store,
IEnumerable<IRoleValidator<BL.Models.Role>> roleValidators,
ILookupNormalizer keyNormalizer,
IdentityErrorDescriber errors,
ILogger<RoleManager<BL.Models.Role>> logger)
: base(store, roleValidators, keyNormalizer, errors, logger) {
}
}
SignInManager
public class SignInManager : SignInManager<BL.Models.User> {
public SignInManager(UserManager<BL.Models.User> userManager,
IHttpContextAccessor contextAccessor,
IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory<BL.Models.User> claimsFactory,
IOptions<IdentityOptions> optionsAccessor,
ILogger<SignInManager<BL.Models.User>> logger,
IAuthenticationSchemeProvider schemeProvider)
: base(userManager, contextAccessor, claimsFactory,
optionsAccessor, logger, schemeProvider) {
}
}
ApplicationUserClaimsPrincipalFactory
public class ApplicationUserClaimsPrincipalFactory :
UserClaimsPrincipalFactory<BL.Models.User, BL.Models.Role> {
public ApplicationUserClaimsPrincipalFactory(UserManager<BL.Models.User> userManager,
RoleManager<BL.Models.Role> roleManager,
IOptions<IdentityOptions> optionsAccessor)
: base(userManager, roleManager, optionsAccessor) {
}
public override async Task<ClaimsPrincipal> CreateAsync(BL.Models.User user) {
var principal = await base.CreateAsync(user);
((ClaimsIdentity)principal.Identity).AddClaims(new[] {
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Uri, user.UserName)
});
return principal;
}
}
3. Configure Startup.cs
Modify ConfigureServices to look like this
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddIdentity<BL.Models.User, BL.Models.Role>()
.AddUserManager<Infrastructure.UserManager>()
.AddRoleManager<Infrastructure.RoleManager>()
.AddSignInManager<Infrastructure.SignInManager>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
var connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IDatabaseConnectionService>(e =>
new DL.Concrete.DatabaseConnectionService(connectionString));
services.AddTransient<IUserStore<BL.Models.User>, BL.Stores.UserStore>();
services.AddTransient<IRoleStore<BL.Models.Role>, BL.Stores.RoleStore>();
services.AddScoped<IUserClaimsPrincipalFactory<BL.Models.User>, Infrastructure.ApplicationUserClaimsPrincipalFactory>();
FixInterfaces(services);
// Add application services.
services.AddTransient<IEmailSender, EmailSender>();
services.AddMvc();
services.AddAutoMapper();
}
private static void FixInterfaces(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IRolesRepository, DL.Repositories.RolesRepository>();
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IUsersClaimsRepository, DL.Repositories.UsersClaimsRepository>();
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IUsersLoginsRepository, DL.Repositories.UsersLoginsRepository>();
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IUsersRepository, DL.Repositories.UsersRepository>();
services.AddTransient<DL.Interfaces.IUsersRolesRepository, DL.Repositories.UsersRolesRepository>();
services.AddTransient<BL.Interfaces.IRoleStore, BL.Stores.RoleStore>();
services.AddTransient<BL.Interfaces.IUserStore, BL.Stores.UserStore>();
}
4. Change AccountController and ManageController
- Replace every ApplicationUser with BL.Models.User. Press Ctrl + H and click on Replace All.
- In AccountController find Register and replace this line with the next one
var user = new BL.Models.User { UserName = model.Email, Email = model.Email };var user = new BL.Models.User { UserName = model.Email, Email = model.Email, Id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString() };
5. Change Views
In Views folder change: Login.cshtml, _LoginPartial.cshtml, _ManageNav.cshtml
@inject SignInManager<ApplicationUser> SignInManager
to
@inject SignInManager<BL.Models.User> SignInManager
and
@inject UserManager<ApplicationUser> UserManager
to
@inject UserManager<BL.Models.User> UserManager
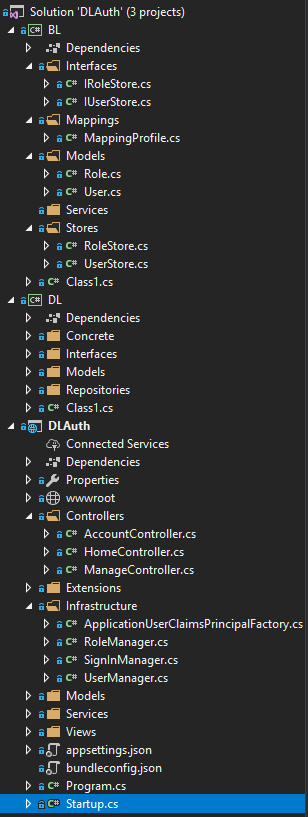
Your final solution should look something like this
Database
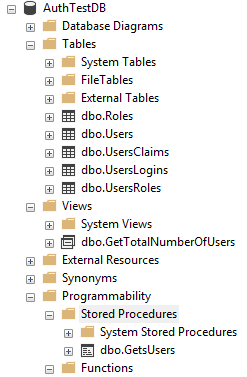
- Create new Database, let’s name it AuthTestDB
- Execute this script to create the tables
- Copy connectionString to appsettings.json
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "Data Source=DELLIRIUM;Integrated Security=False;User ID=testuser;Password=Password12345;Connect Timeout=30;Initial Catalog=AuthTestDB;Encrypt=False;TrustServerCertificate=True;ApplicationIntent=ReadWrite;MultiSubnetFailover=False" }, "Logging": { "IncludeScopes": false, "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } } }Your DB should look like this
Final
You can now try to register new account, and log in.